Generate PELE parameter files¶
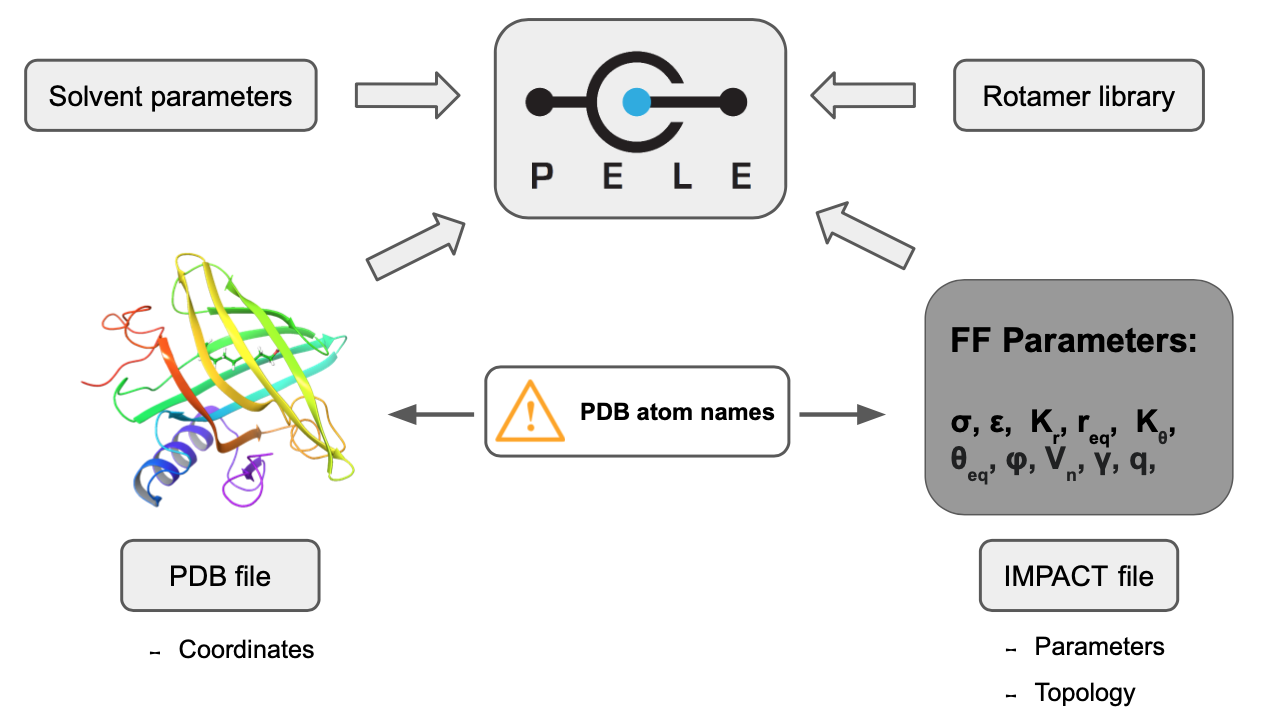
The main purpose of peleffy is to build the parameter files for PELE. Basically, PELE requires two files for each non-standard residue found in the system:
IMPACT template: a file containing the atom types and parameters of the ligand. Its job is to link each atom with the corresponding parameters using PDB atom names. Thus, PDB atom names in the input PDB file must match with the expected PDB atom names in the Impact file. This file intrinsically contains the information about the topology and connectivity of each residue.
Rotamer library: a file containing the branches that can rotate with respect to a central atomic core. Each branch consists in a set of consecutive rotatable bonds.
Besides, a third file with the Solvent parameters might be required when employing the OBC implicit solvent.
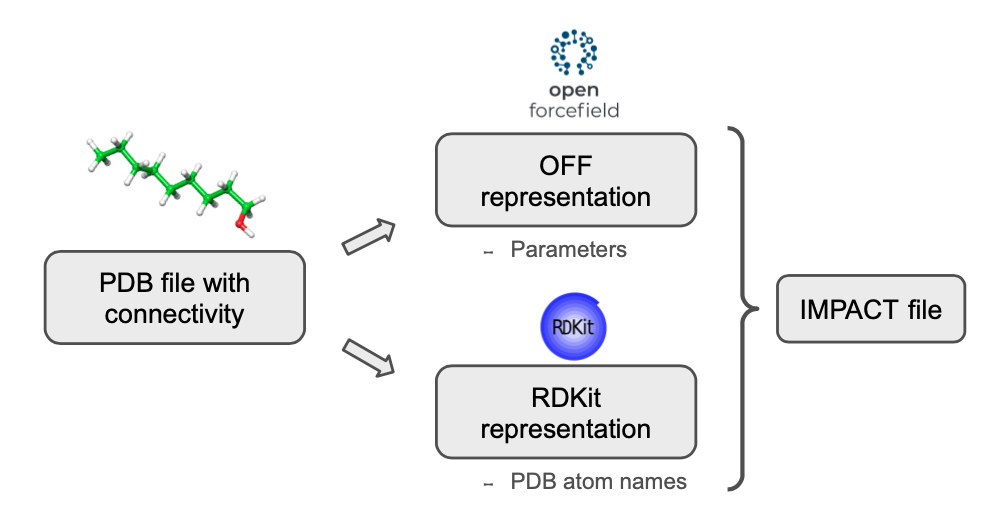
The Open Force Field Toolkit is employed to assign the parameters to each atom according to its chemical environment. Besides, the PDB atom names are stored using RDKit. With this dual molecular representation, peleffy can run the parameterization workflow of Open Force Field while tracking the PDB atom names with RDKit.
Basic usage¶
The more straightforward way to install peleffy along with the required dependencies is through the command-line interface built in main.py module. Therefore, the parameter files for a particular ligand can be obtained with:
$ python -m peleffy.main my_ligand.pdb
------------------------------------------------------------
Open Force Field parameterizer for PELE 1.1.0
------------------------------------------------------------
- General:
- Input PDB: my_ligand
- Output path: None
- Write solvent parameters: False
- DataLocal-like output: False
- Parameterization:
- Force field: openff_unconstrained-1.3.0.offxml
- Charge method: am1bcc
- Rotamer library:
- Resolution: 30
- Exclude terminal rotamers: True
------------------------------------------------------------
- Initializing molecule from PDB
- Loading molecule from RDKit
- Assigning stereochemistry from 3D coordinates
- Setting molecule name to 'ligand'
- Setting molecule tag to 'LIG'
- Representing molecule with the Open Force Field Toolkit
- Generating rotamer library
- Core set to the center of the molecule
- Loading 'openff_unconstrained-1.3.0.offxml'
- Parameterizing molecule
- Parameters were built successfully:
- 12 atoms
- 12 bonds
- 18 torsions
- 24 propers
- 6 impropers
- Generating solvent parameters
- All files were generated successfully:
- /Users/martimunicoy/repos/BSC/peleffy/LIG.rot.assign
- /Users/martimunicoy/repos/BSC/peleffy/ligz
- /Users/martimunicoy/repos/BSC/peleffy/ligandParams.txt
------------------------------------------------------------
Command-line arguments¶
Almost all the important settings can be tuned up through command-line arguments. To obtain the full list of flags you can type:
$ python -m peleffy.main --help
usage: main.py [-h] [-f NAME] [-r INT] [-o PATH] [--with_solvent]
[--as_datalocal] [-c NAME] [--include_terminal_rotamers]
PDB FILE
positional arguments:
PDB FILE Path PDB file to parameterize
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-f NAME, --forcefield NAME
OpenForceField\'s forcefield name. Default is
openff_unconstrained-1.2.0.offxml
-r INT, --resolution INT
Rotamer library resolution in degrees. Default is 30
-o PATH, --output PATH
Output path. Default is the current working directory
--with_solvent Generate solvent parameters for OBC
--as_datalocal Output will be saved following PELE's DataLocal
hierarchy
-c NAME, --charge_method NAME
The name of the method to use to compute charges
--charges_from_file PATH
The path to the file with charges
--chain CHAIN Chain of the molecule to parameterize
--include_terminal_rotamers
Not exclude terminal rotamers when building the
rotamer library
Find below the complete list of command-line arguments in full detail.
PDB file¶
It is a mandatory positional argument that points to the PDB file which contains ligand to parameterize.
Flag:
PDB FILEType:
stringExample: the code below will run peleffy to parameterize the ligand at path/to/my_ligand.pdb
$ python -m peleffy.main path/to/my_ligand.pdb
Force field¶
It defines the force field to employ to parameterize the ligand. It can be any supported force field shipped by the OpenFF toolkit or the Schrodinger’s OPLS2005.
Warning
Working with Schrodinger’s OPLS2005 requires a valid Schrodinger installation with the ffld_server. An environment variable called SCHRODINGER must be set, pointing to the Schrodinger’s installation path.
Flag:
-f NAME,--forcefield NAMEType:
stringDefault:
openff_unconstrained-1.2.0.offxmlExample: the code below will run peleffy using the forcefield named as ‘openff_unconstrained-1.0.0.offxml’
$ python -m peleffy.main path/to/my_ligand.pdb -f openff_unconstrained-1.0.0.offxml
Rotamer library resolution¶
It defines the resolution, in degrees, to use in the rotamer library.
Flag:
-r INT,--resolution INTType:
intDefault:
30Example: the code below will run peleffy using a resolution of 60 for the rotamer library
$ python -m peleffy.main path/to/my_ligand.pdb -r 60
Output path¶
It defines the output path where the resulting files will be saved.
Flag:
-o PATH,--output PATHType:
stringDefault:
., the current working directoryExample: the code below will save the results into my_custom_folder/
$ python -m peleffy.main path/to/my_ligand.pdb -o my_custom_folder
Include solvent parameters¶
It also generates the OBC solvent parameters and saves them into the output location.
Flag:
--with_solventDefault:
False, do not includeExample: the code below will generate and save the OBC solvent parameters
$ python -m peleffy.main path/to/my_ligand.pdb --with_solvent
Save output as DataLocal¶
It saves the output files following the DataLocal hierarchy expected by PELE.
Flag:
--as_datalocalDefault:
False, do not save output files as DataLocalExample: the code below will generate and save output files following the DataLocal hierarcy of PELE
$ python -m peleffy.main path/to/my_ligand.pdb --as_datalocal
Charge method¶
It sets the method to compute the partial charges.
Flag:
-c NAME,--charge_method NAMEType:
stringChoices: one of [
gasteiger,am1bcc,OPLS]Default:
am1bccExample: the code below will calculate partial charges using ‘gasteiger’ method
$ python -m peleffy.main path/to/my_ligand.pdb -c gasteiger
Charge from file¶
It sets the method to load external partial charges.
Flag:
--charges_from_file PATHType:
stringDefault:
NoneExample: the code below will load the partial charges from a MAE file
$ python -m peleffy.main path/to/my_ligand.pdb --charges_from_file path/to/my_ligand.mae
Chain¶
It defines the chain of the molecule to parameterize from the input PDB file. This flag has to be used if the input PDB file contains multiple chains, if no chain is supplied a PDB with a single chain is expected.
Flag:
--chainDefault:
NoneExample: the code below will parameterize the hetero molecule in the chain L of the input file
$ python -m peleffy.main path/to/my_system.pdb --chain L
Include terminal rotamers¶
It always includes terminal rotamers, even if they belong to a terminal methyl group whose rotation is trivial in PELE.
Flag:
--include_terminal_rotamersDefault:
False, exclude terminal rotamersExample: the code below will generate a rotamer library including all terminal rotamers
$ python -m peleffy.main path/to/my_ligand.pdb --include_terminal_rotamers
AMBER-compatible template¶
It generates an Impact template that will be compatible with PELE’s AMBER force field implementation. The default template is compatible with OPLS’s implementation.
Flag:
--for_amberDefault:
False, compatible with OPLSExample: the code below will generate an Impact template compatible with PELE’S AMBER
$ python -m peleffy.main path/to/my_ligand.pdb --for_amber